Aging results in a gradual loss of skeletal muscle function over time. Sarcopenia, the progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, and performance with age, is one of the critical causes of functional decline in aged adults. Essential for supporting breathing, as well as moving and maintaining posture and balance, skeletal muscle makes up nearly 40% of a young, healthy individual’s total body mass and decreases between 3 to 8% each decade after 30 years of age.
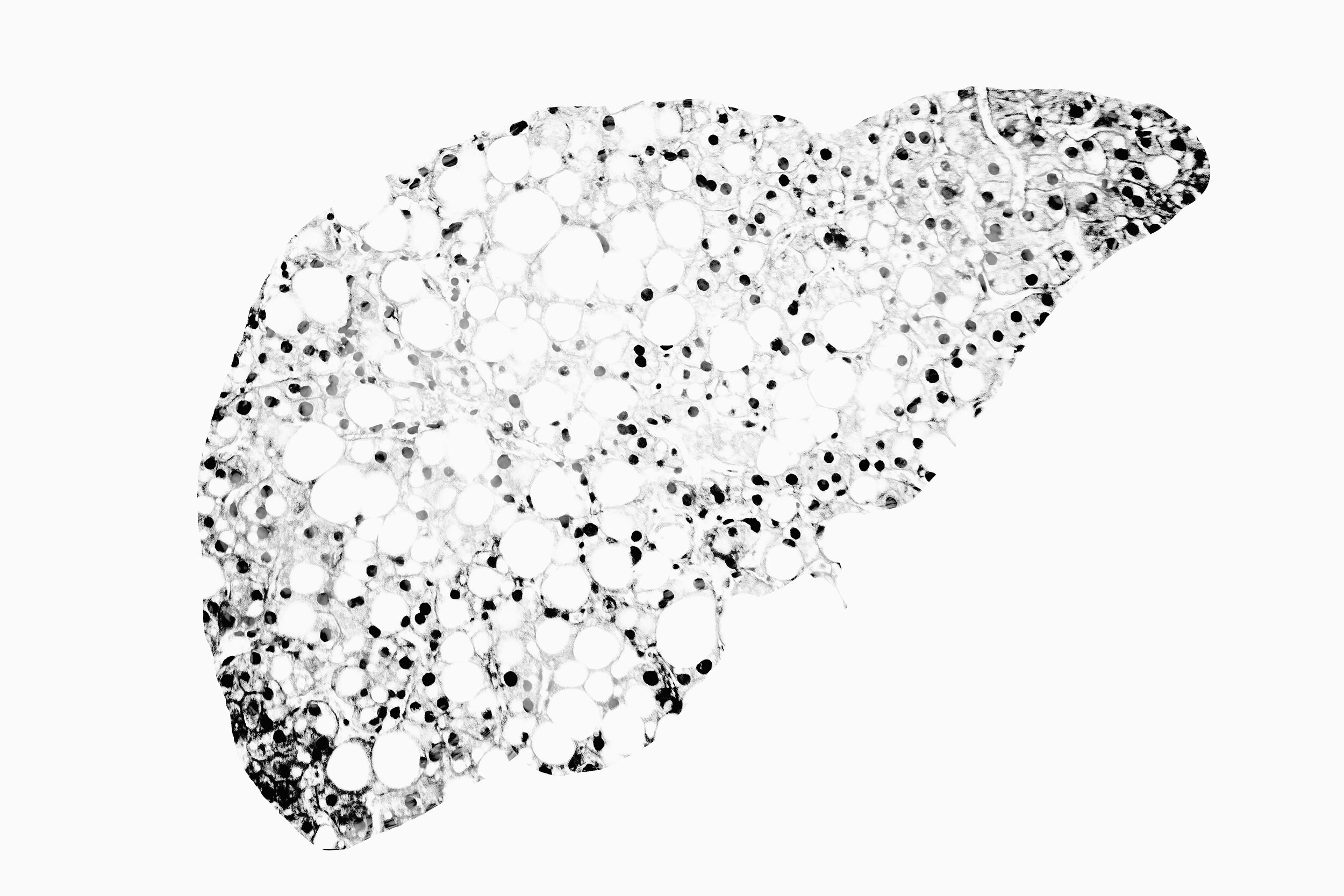
Read MoreA recent phase 2 clinical trial published on Cell Press Sneak Peek, a preprint publication website for papers under review by Cell Press Journals, found that a novel combined metabolic cofactor supplement (CMCS) cocktail which included nicotinamide riboside (NR) significantly reduced hepatic fat in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients by 10%.
Read MoreResults of a phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial assessing whether a mixture of Combined Metabolic Activators (CMAs) targeted at mitochondrial function, could improve metabolic function and aid the recovery of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 infected individuals, are now available in the peer-reviewed journal Advanced Science.
The study, conducted at Umraniye Teaching and Research Hospital, University of Health Sciences, Istanbul, Turkey, found that the CMAs, which included nicotinamide riboside (NR), L-serine, N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), and L-carnitine tartrate, when delivered in combination with standard of care, experienced a statistically significant, 3.5 day reduction in recovery time in the COVID-19 infected patients.[1]
Read MoreA recent study published in The European Molecular Biology Organization Journal, conducted by investigators at the National Institute on Aging (NIA) and the National Cancer Institute (NCI), both divisions of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has uncovered some important findings related to the relationship between critically short telomere length and telomere dysfunction, the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) metabolome, mitochondrial maintenance, and replicative senescence (a phenomenon where normal cells stop dividing.)
Read MoreA new study published in Experimental Gerontology found that among 170 blood donors, elderly patients with heart failure had the lowest NAD+ levels, which suggests a role for NAD+ precursors in supporting heart health [1].
Read MoreOn the heels of two previously published preclinical studies investigating the effect of viral infection on NAD+ levels, new clinical research in 93 mild-to-moderate COVID-19 infected patients is now available on the open access preprint publication server medRxiv.org.
Read MoreA study published in Translational Animal Science finds that in ovo nicotinamide riboside (NR) injections increased chick pectoralis major (PM) muscle weight, length, width, and depth – a result which could have a big impact on the poultry industry.
Read MoreA recent study found that raising NAD+ levels in a mouse model could protect the survival and function of retinal cells, the cells responsible for sight, against damaging UV light.
Read MoreRaising NAD+ levels with the precursor Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) was found to reduce markers of inflammation in the blood from a small group of Stage D heart failure (HF) patients.
A new study shows that while both nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and nicotinamide riboside (NR) can help protect against blood-vessel inflammation by raising NAD+, NR may be the more direct and effective precursor.
Recent studies have shown that increasing cellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels can restore metrics of fertility, such as oocyte (immature egg) count and health, among aging mice.
The human body is composed of cells in the trillions. Each cell relies on a resource molecule called NAD+ for the generation of energy we know as ATP. This energy helps cells perform their unique functions and survive. As the available knowledge of NAD+ expands, scientists have come to realize that it also plays a vital role in helping activate important signaling molecules for cellular defense.
Read MoreMost of us are aware there are steps we can take to support the health of our hearts, teeth, eyes, and other vital organs. But when it comes to our brains, we’re often stumped.
Read MoreOver the last several years there has been an influx of research started on nicotinamide riboside (NR) due to its unique mechanism for raising levels of the coveted compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).
Read MoreMetabolism is often thought of as the way our bodies process the foods we eat. We’ve all heard that a “slow” metabolism may lead to weight gain and that those people who never seem to struggle with weight may have “fast” metabolisms. But what does the word metabolism even mean and what does it affect outside of our waistlines?
Read MoreClinical trials in humans are essential to substantiating the health benefits of supplements. They provide important scientific evidence of effectiveness and safety. But how do researchers know what doses to use and what possible side effects to look out for in these trials?
Read MoreAlzheimer’s disease is a chronic condition in which a person’s cognitive functions, such as memory, language, and mood, decline with increasing age.
Read MoreIn a paper published in the journal PNAS, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis reported that glioblastoma tumors over-produce NAMPT, an enzyme which is involved in the creation of NAD.
Read MoreIn a paper published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, researchers at Aristotle University of Thessaloniki in Serres, Greece reported that rats who received NR tended to show worse physical performance by 35%. There are a number of things to be aware of as you read this study and digest its conclusion.
Read More