Ataxia telangiectasia (AT) is a rare, inherited neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cerebellar degeneration, immunodeficiency, and cancer predisposition. Previous preclinical research has shown that increasing NAD+ through nicotinamide riboside (NR), a vitamin B3 form, improved neurodegeneration and neuromuscular function in mouse models of AT. These results indicate that NAD+ boosting may be a potential therapeutic strategy for AT. Researchers of this study set out to investigate the effects of boosting NAD with NR in AT patients.
Read MoreA recent phase 2 clinical trial published on Cell Press Sneak Peek, a preprint publication website for papers under review by Cell Press Journals, found that a novel combined metabolic cofactor supplement (CMCS) cocktail which included nicotinamide riboside (NR) significantly reduced hepatic fat in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients by 10%.
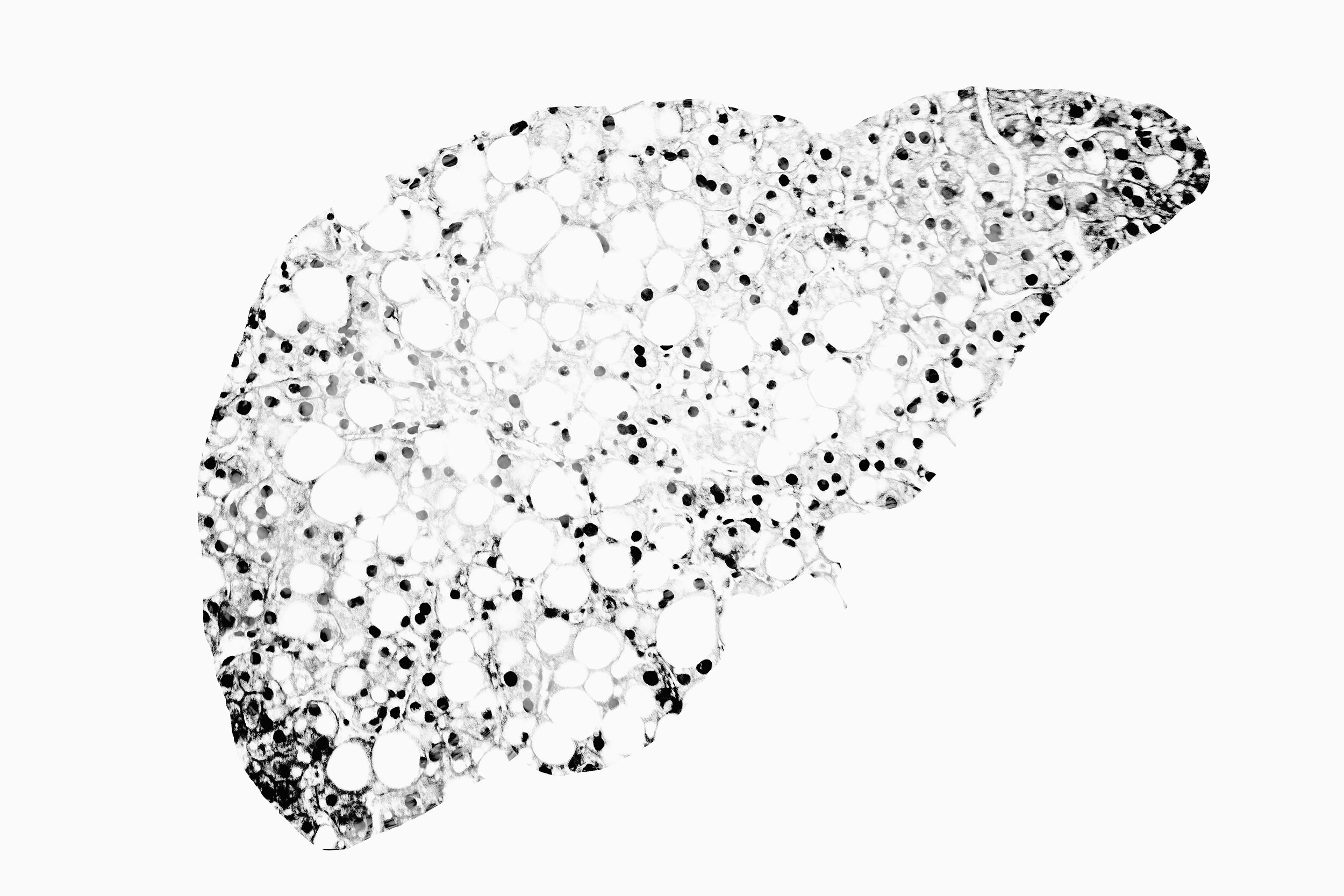
Read MoreA new study recently published in Hepatology Communications and conducted by investigators from The University of Birmingham, its affiliated hospital, and the University of Iowa, found that NAD+ levels were significantly reduced in liver samples obtained from those undergoing transplant surgery for alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), suggesting that NAD+ may play a critical role in mitigating liver damage.
Read MoreA clinical study conducted at the University of Copenhagen, Aarhus University Hospital and the University of Iowa has provided the first human evidence of the potential for nicotinamide riboside (NR) to improve human health in obesity.
Read More